Blockchain and its application in the energy sector
By Mari Kristine Buckholm, Smart Innovation Norway 25. May 2018
Blockchain is one of the world’s leading software platforms for digital assets, and the new technology can be used to build a radically better financial system.
Blockchain technology has become known to more and more people in all corners of the world over the past few years. But, what is it exactly?
Sea of possibilities
A blockchain is defined as a digitized, decentralized, public ledger of all cryptocurrency transactions. This new technology is a perfect example of the ongoing digitalization wave and represents endless possibilities, pros and cons included:
“Blockchain is decentralized and highly transparent, because anyone with access to a blockchain can view the entire chain. That also means that security is good, it relies on cryptographic algorithms that make it very difficult to malicious changes in the ledger,” explains Terese Troy Prebensen, CEO of Fredrikstad Energi Marked.

CEO of Fredrikstad Energi Marked AS, Terese Troy Prebensen.
The cons of blockchain, on the other hand, are related to energy consumption, lack of regulation and exchange fees.
Unique energy solutions
Today, blockchain technology does not yet play a significant role in the energy sector.
«With a blockchain, many people can write entries into a record of information, and a community of users can control how the record of information is amended and updated. That means it’s possible to do transactions of energy from consumer to consumer, but the regulation of energy transmission with grid hire does not benefit from this today,” notes Troy Prebensen.
However, she is convinced blockchain technology will radically benefit the energy sector in the near future.
“With smart neighborhoods, blockchain can get a unique settlement solution in areas where energy can be produced and traded locally. This requires changes to the grid regulations, or new forms of contracts between areas / neighborhoods and the grid company,” the CEO emphasizes.
What is blockchain?
- A blockchain is a digitized, decentralized, public ledgerof all cryptocurrency transactions.
- Constantly growing as ‘completed’ blocks(the most recent transactions) are recorded and added to it in chronological order, it allows market participants to keep track of digital currency transactions without central recordkeeping.
- Each node (a computer connected to the network) gets a copy of the blockchain, which is downloaded automatically.
- Originally developed as the accounting method for the virtual currency Bitcoin, blockchains – which use what’s known as distributed ledgertechnology (DLT) – are appearing in a variety of commercial applications today.
- Currently, the technology is primarily used to verify transactions within digital currencies, though it is possible to digitize, code and insert practically any document into the blockchain.
- Doing so creates an indelible record that cannot be changed; furthermore, the record’s authenticity can be verified by the entire community using the blockchain instead of a single centralized authority.
Social media
INVADE updates

It is possible to control the speed of charging electric cars on a large scale with algorithms. This can be concluded from the results of a Smart Charging test on 700 public charging stations as part of the Horizon 2020 INVADE project. (4 years ago)

“I found the INVADE pilots incredibly interesting”
During the European Utility Week in Paris in November 2019, the INVADE project presented itself in a unique way in the EU Projects Zone. Using videos and an informative quiz, the INVADE stand was always busy. (4 years ago)

“Solutions like INVADE are necessary”
The Horizon 2020 INVADE project is coming to an end this year. Last week, a conference and a workshop were organized on behalf of the project and parallel to event Smart City Expo World Congress in Barcelona. (4 years ago)

The INVADE project has resulted in five successful pilot stories and professional films have been made from each pilot site. You can watch them all here. (4 years ago)
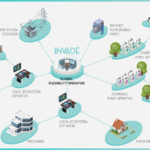
The work package WP9: Business models and market structures, led by INVADE project partner Lyse has put forward a market structure for platform-based business models inspired by disruptive companies like Amazon and Airbnb. (4 years ago)

In the end of May, the INVADE consortium was gathered in the Netherlands. During the two-day meeting, all five pilot owners presented their progress to the project partners. (4 years ago)

Badenova sells and operates networks, energy storages and smart city infrastructures in a region of nearly 1 million inhabitants and adapts INVADE technology and solutions on site for its customers. (4 years ago)

“We will act on everything we have heard today”
When Norway’s Standing Committee on Energy and the Environment visited Smart Innovation Norway headquarters in Halden on Monday, they were introduced to the company’s unique EU research expertise. (5 years ago)

Energy businesses that manage to incorporate total social impact into their activities, products, services, and communication to customers and employees, will have the best premises for future business growth – and for contributing to a better world. (5 years ago)

What is the added value?
In a few weeks the INVADE integrated platform will be up and running and the pilot owners are both hopeful and excited about what the results will show. (5 years ago)